Macos Install Software With Sudo
- Macos Install Software With Sudo Windows 10
- Install Sudo Linux
- Sudo Install Pip
- Ubuntu Install Sudo
- Macos Sudo Without Password
These advanced steps are primarily for system administrators and others who are familiar with the command line. You don't need a bootable installer to upgrade macOS or reinstall macOS, but it can be useful when you want to install on multiple computers without downloading the installer each time.
Download macOS
I am on macOS Sierra version 12.10.16. I downloaded an application. This app has.dmg extension. I would like to install it without using sudo or without being one of the sudo users. When I do hdi. Codespaces CLI Reference.; 2 minutes to read; In this article Installation Windows Install via Powershell. Download and execute the PowerShell script to install the Codespaces CLI. Homebrew is the easiest way to manage your CLI install. Jan 19, 2018 But, one of the best things about using a Mac is how easy it is to install software. And removing most software packages on macOS is just as easy.
Find the appropriate download link in the upgrade instructions for each macOS version:
macOS Catalina, macOS Mojave, ormacOS High Sierra
Installers for each of these macOS versions download directly to your Applications folder as an app named Install macOS Catalina, Install macOS Mojave, or Install macOS High Sierra. If the installer opens after downloading, quit it without continuing installation. Important: To get the correct installer, download from a Mac that is using macOS Sierra 10.12.5 or later, or El Capitan 10.11.6. Enterprise administrators, please download from Apple, not a locally hosted software-update server.
OS X El Capitan
El Capitan downloads as a disk image. On a Mac that is compatible with El Capitan, open the disk image and run the installer within, named InstallMacOSX.pkg. It installs an app named Install OS X El Capitan into your Applications folder. You will create the bootable installer from this app, not from the disk image or .pkg installer.
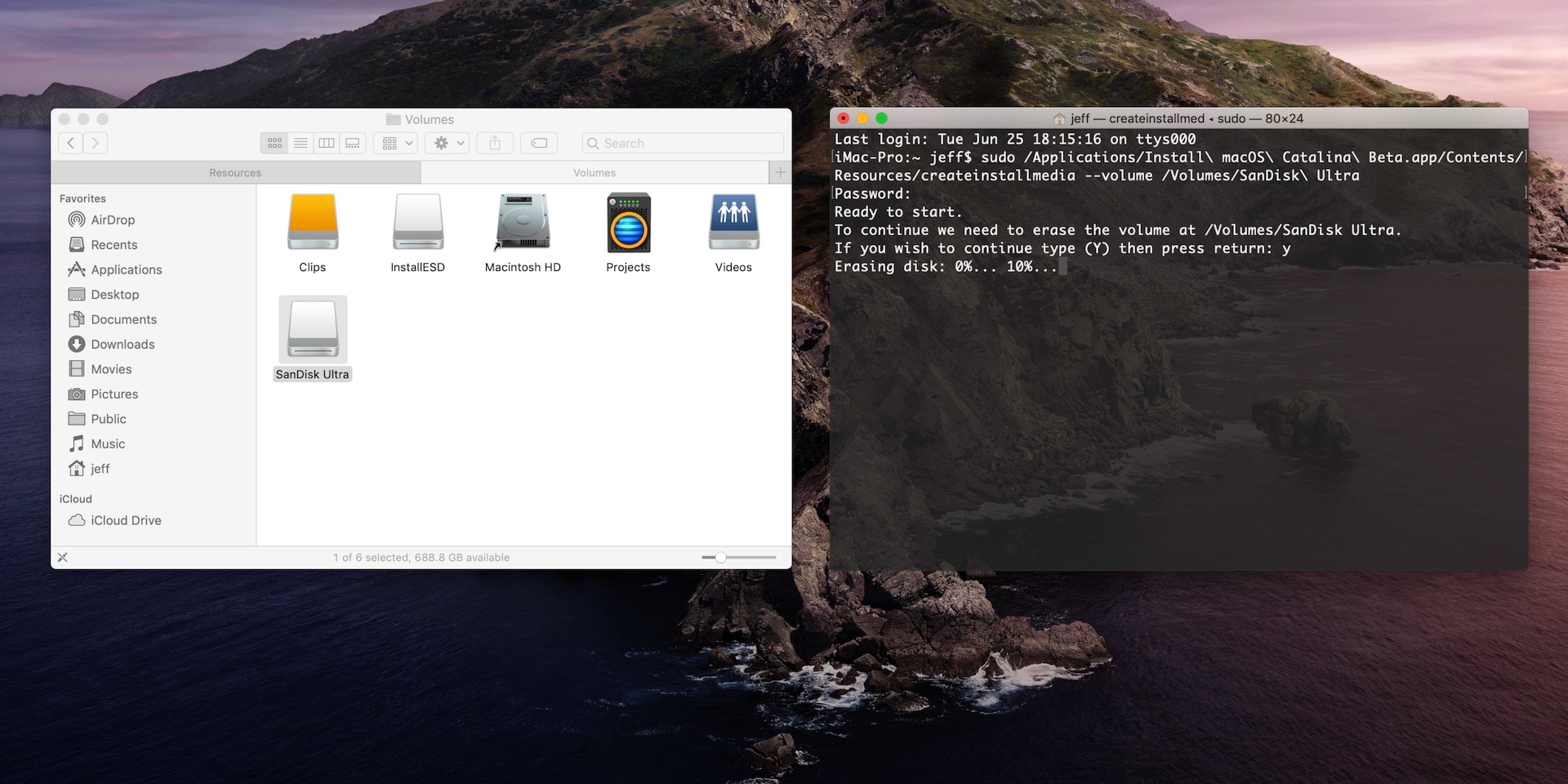
Use the 'createinstallmedia' command in Terminal
- Connect the USB flash drive or other volume that you're using for the bootable installer. Make sure that it has at least 12GB of available storage and is formatted as Mac OS Extended.
- Open Terminal, which is in the Utilities folder of your Applications folder.
- Type or paste one of the following commands in Terminal. These assume that the installer is still in your Applications folder, and MyVolume is the name of the USB flash drive or other volume you're using. If it has a different name, replace
MyVolumein these commands with the name of your volume.
Catalina:*
Mojave:*
High Sierra:*
El Capitan: - Press Return after typing the command.
- When prompted, type your administrator password and press Return again. Terminal doesn't show any characters as you type your password.
- When prompted, type
Yto confirm that you want to erase the volume, then press Return. Terminal shows the progress as the bootable installer is created. - When Terminal says that it's done, the volume will have the same name as the installer you downloaded, such as Install macOS Catalina. You can now quit Terminal and eject the volume.
* If your Mac is using macOS Sierra or earlier, include the --applicationpath argument, similar to the way this argument is used in the command for El Capitan.
Use the bootable installer
After creating the bootable installer, follow these steps to use it:
- Plug the bootable installer into a compatible Mac.
- Use Startup Manager or Startup Disk preferences to select the bootable installer as the startup disk, then start up from it. Your Mac will start up to macOS Recovery.
Learn about selecting a startup disk, including what to do if your Mac doesn't start up from it. - Choose your language, if prompted.
- A bootable installer doesn't download macOS from the Internet, but it does require the Internet to get information specific to your Mac model, such as firmware updates. If you need to connect to a Wi-Fi network, use the Wi-Fi menu in the menu bar.
- Select Install macOS (or Install OS X) from the Utilities window, then click Continue and follow the onscreen instructions.
Learn more
Macos Install Software With Sudo Windows 10
For more information about the createinstallmedia command and the arguments that you can use with it, make sure that the macOS installer is in your Applications folder, then enter this path in Terminal:
Install Sudo Linux
Catalina:
Mojave:
High Sierra:
El Capitan:
-->Installation
Windows
Install via Powershell
Download and execute the PowerShell script to install the Codespaces CLI.
macOS
Homebrew is the easiest way to manage your CLI install. It provides convenient ways to install, update, and uninstall. If you don't have homebrew available on your system, install homebrew before continuing.
You can install the CLI by updating your brew repository information, and then running the install command:
Linux
Install via apt
Add the public key for the microsoft repo:
Add the necessary repo for your release:
Ubuntu
- Ubuntu 18.04:
- Ubuntu 16.04:
- Ubuntu 14.04:
Debian
Debian 10:
Debian 9:
Debian 8:
Update apt-get:
Install the Codespaces CLI:
For other Linux distributions, run the following script by using curl and pipe directly to bash, or download the script to a file and inspect it before running.
Usage
Codespaces is launched using the following command:
The following options can be provided to Codespaces:
-v | --versionDisplays the current installed version of the CLI-? | -h | --helpPrints out help information for the command
The following commands are available:
startBegins the interactive process of registering your self-hosted machine. For more information, see Start Codespaces.stopRemoves your machine from Visual Studio Codespaces
Start Codespaces
The start command begins the interactive process of registering your self-hosted machine:
These arguments can be provided to the start command:
Sudo Install Pip
Note
You can either specify your plan by supplying either the subscription, resource group, and name or the plan id.
Ubuntu Install Sudo
-s | --subscriptionThe Subscription of the plan this environment should be registered to-r | --resource-groupThe Resource Group of the plan this environment should be registered to-p | --plan-nameThe existing plan name this environment should be registered to-i | --plan-idThe fully qualified plan id ('/subscriptions/...')-w | --workspace-pathThe workspace path. By default, the CLI will use the current working directory as the landing point when you connect. You will be able to switch folders after connection.-n | --nameThe environment name-v | --serviceIf supplied, runs the local agent as a service/daemon on this machine (Requires admin/sudo privileges on Windows and OSX)-? | -h | --helpShow help information
Stop Codespaces
Macos Sudo Without Password
The stop command removes your environment from the Visual Studio Codespaces service: